YOUR LOCAL DIGITAL MARKETING AGENCY
Category Archives: TECHNOLOGY
What is the Internet of Things (IoT)? The Internet of Things, often abbreviated as IoT, is a revolutionary concept that describes the interconnection…
Introduction to MERN Stack Interview Questions The MERN stack interview questions is a popular choice for developers building modern web applications. Its appeal…
1. Introduction to Tiranga Games The Tiranga Games: Uniting India Through Sports is an extraordinary initiative that brings together people from all walks…
1. Introduction to Consumer Technology Consumer technology encompasses a wide range of electronic devices, software, and services designed for personal use. These technologies…
1. Introduction to Automation in Information Technology Automation in Information Technology (IT) refers to the use of technology to perform tasks that would…
Introduction to Social Media Marketing Why Social Media Marketing Matters in 2024 In 2024, social media marketing continues to be a vital part…
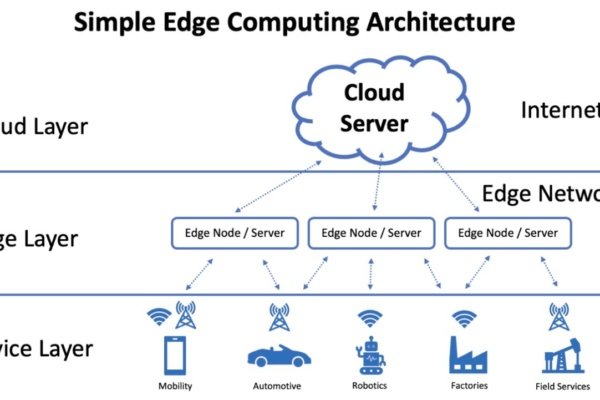
1. Introduction to Edge Computing Definition and Overview What is Edge processing is a paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to…
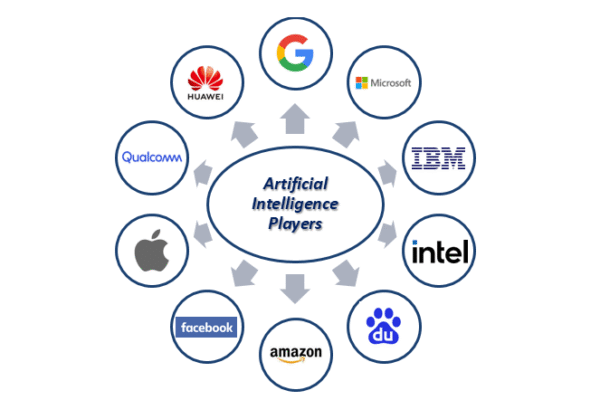
In today\'s rapidly evolving technological landscape, AI companies are at the forefront of innovation, leveraging advanced algorithms and data analytics to transform industries…
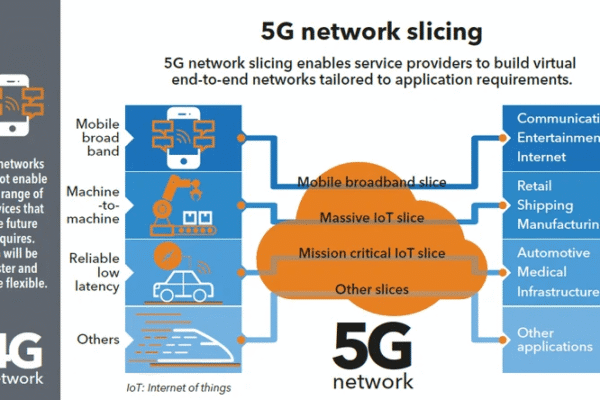
Introduction to Network Slicing in 5G Networks 5G Network Virtualization is a groundbreaking technology that allows the creation of multiple virtual networks on…
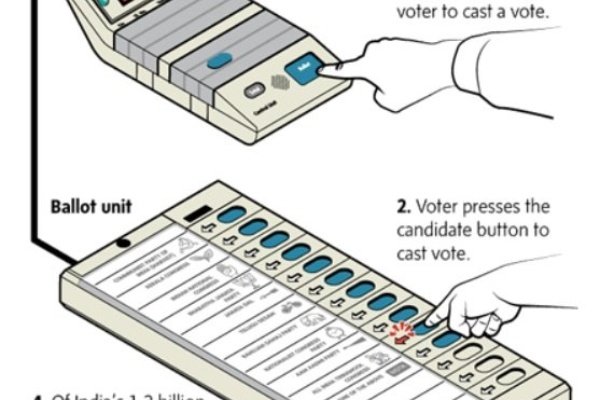
Electronic Voting Machine (EVM) hardware refers to the physical components that make up the EVM system used in elections. The hardware is designed…
Your business isn't a template, so why is your digital presence? We move beyond 'one-size-fits-all' solutions. At rdm tech, we custom-craft your website, app, and marketing from the ground up to be as unique as your brand.